2. Plate-type?evaporator
 Equipment principle
Equipment principle
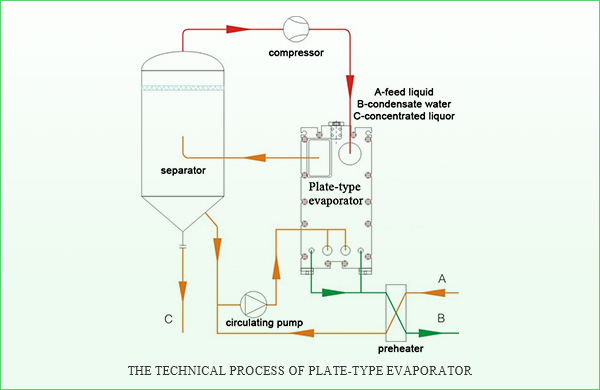
The plate evaporator is a new type of high-efficiency evaporator formed by stacking a series of corrugated metal sheets. Thin rectangular channels are formed between plates, and heat is transferred through the plates as the thin film to achieve evaporation. The solution to be vaporized is heated and boiled in the evaporator, and then vaporizes quickly. The evaporation will drive the feed liquid to rise, and a liquid film is formed along the inner surface of the heat exchange. The feed liquid flows through the heated surface in the form of a liquid film, which quickly evaporates and vaporizes. The heating time gets shorter, but the effect becomes more excellent. The equipment has the characteristics of high heat transfer capability, strong evaporation strength and short contact time.
Equipment features
 Advantages:
Advantages:
1. High heat transfer efficiency.
2. low heat loss, low energy consumption and low operating cost.
3. Not be easy to form deposition and not easy to block.
4. Less space demand and useful for the expansion and maintenance later.
5. Safe and reliable, improving product quality.
6. low civil construction cost.
7. High degree of automation is conducive to the construction of intelligent workshops and reformation for old workshops.
8. Equipment maintenance is simple and economical, and the average operating cost is low.
9. Our team has rich experience both in installation and commissioning on the site. In addition, our company has perfect service system after sale.
 Disadvantages:
Disadvantages:
There are certain restrictions on the concentration of the product. Compared with the tube evaporators, the concentration of the product is low after the concentration.
 Application
Application
Plate-type evaporator used in F55

 The plate-type evaporator is widely used in the fields as follows.
The plate-type evaporator is widely used in the fields as follows.
-Sugar industry
starch sugar, including glucose, dextrose monohydrate, fructose, crystalline fructose, F42, F55, maltose, dextrin, etc.; xylose.
-Chemical industry
Organic acids include L-lactic acid, citric acid, VC, monosodium glutamate, and various amino acids, such as lysine, L-phenylalanine, leucine, methionine, etc.
-Food industry
Stevia sugar, sorbitol, and xylitol and sodium erythorbate, etc.
-Pharmaceutical industry
antibiotics, etc.
-Environmental protection industry��,
wastewater treatment, etc.





